As we all know there are five main types of inks used for printing textiles digitally. Reactive, Acid, Direct Disperse, Sublimation & Pigment inks. Each of the ink has a method of printing, curing & fixation associated with it. Except for the pigment, all of the above are fixed by chemical bonding with the fabric fibers.
The purpose of this article is to understand how the Digital Textile Pigment ink works with the fabric & understand what all variables have an impact on this process. Before we start that let’s start with the quality criteria of printed fabrics.
Performance of printed fabric (by any method) is evaluated by few important criteria such as Color Fastness, Wash Fastness, Wet & Dry Rub Fastness, Perspiration Fastness, Hand Feel & Safety aspects associated with the colorants & ink formulations. Let’s understand how in general digital textile pigment inks fare on each of these aspects. Thanks to highly fade-resistant pigments, these inks have excellent Color Fastness to fading. The latest advancements in ink formulations offer highly reliable performance for Washing Fastness along with Wet & Dry Rub Fastness. Pigment inks offer very good perspiration fastness as well. The only downside of the pigment printed fabrics is they have a slight feel or hand on printed area.
Pigment inks are fixed by creating adhesion of the pigment with the fabric. Pigment inks contain binder which typically is polymer-based compound. During the fixation process this polymer is heated to a temp where it plasticizes (gets converted to semi solid-state) and then creates a bond between fibers of fabric and pigment particles in the ink. This in a sort creates a physical bond between the pigment particle and the fabric. This binder plays a highly critical role in the performance of the pigment inks. Right from ink stability, nozzle jetting performance, preventing clogging of the print-head to ensuring fastness of the inks on fabric, having minimum feel are various things depending on the binder. Managing all this is a tough challenge & that’s why finding a good pigment ink becomes difficult.
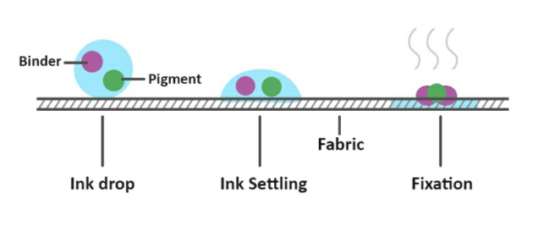
Interestingly this process of binding gives pigment inks some unique advantages. Most importantly the curing process can be done with the exposure of printed fabric to heat. Right temp for sufficient time is all you need to make ink fix to the fabric. This saves a tremendous amount of water required for other printing techniques. In addition, you can use pigment inks to print on various fabrics even with blended compositions. This opens up possibilities of printing blended fabrics digitally. In addition, some applications where it is not desired to process fabrics after printing, pigment inks are used extensively.
From the printing process perspective, PFP fabrics are required to start with. “PFP” or “Prepared For Print” fabrics generally are processed to remove various oils, waxes, sizing agents, etc used during various stages of manufacturing. These chemicals interact and prevent proper fixation of the inks. A significant portion of the industry pre-coats the fabric before printing. Here’s how an ideal flow of printing would look like.
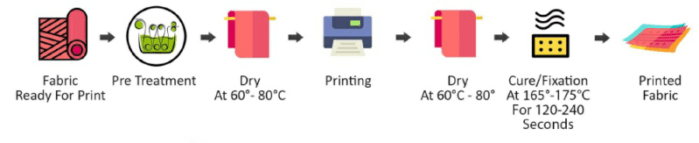
Digital textile pigment inks are supposed to be capable of printing directly on fabrics without any pretreatment. It’s an absolute fact but it doesn’t really say anything about the print results. It would be interesting to understand the role of pretreatment. As you are aware pigment inks are used primarily to print on natural fiber-based fabrics. When printed on fabric directly, the pigment particles are absorbed by the porous fibers of the fabric. So while results look good at the time of printing, they look faded once the print is cured. This is where the role of pretreatment comes into the picture.
Pretreatment chemicals depending upon the chemical base, perform various functions. Primarily all of them help to retain the inks on the surface of the fabrics. This prevents ink absorption into the fibers. Retention of more ink on top of the fibers helps inks produce bright colors. Some pretreatments go further and assist to improve the fixation of the inks to fabrics. Thereby improving wash, wet rub & dry run fastness properties of the inks. In addition, you can use less amount of ink and fewer print passes if the fabric is pre-coated. This helps to improve productivity and reduce ink costs.
I hope this article offers clarity about the working of digital textile pigment inks. Please feel free to get in touch with us at Splashjet in case you would be interested to know more about our range of digital textile pigment inks.




